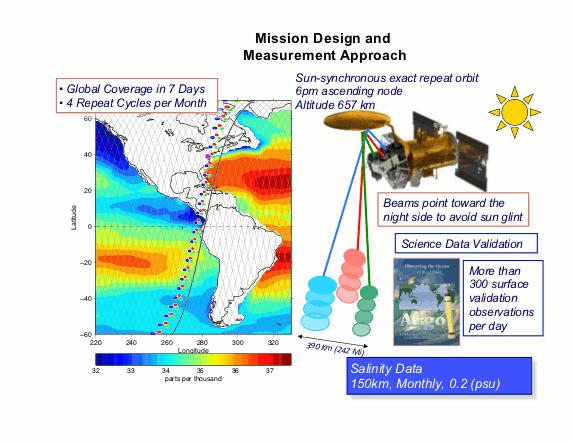
The Aquarius/SAC-D mission concept. The satellite is in a polar sun-synchronous orbit crossing the equator at 6pm (ascending) and 6am (descending) local time. The Aquarius sensor views continually away from the sun to avoid signal contamination from solar L-band energy flux. The three beams vary in width and incidence angle to form a 390 km wide ground swath. The orbit has an exact repeat ground track every seven days, with 390 km track spacing at the equator, ensuring complete global coverage of the swath. Salinity data calibration and validation will be based on available in situ surface measurements by ships, buoys and Argo floats.
Instrument Mode: Active/Passive L-band, Push-broom measurement approach using 3-beam, offset antenna.
Orbit: 657 km, sun synchronous @ 6 pm, ascending node
Observatory: CONAE contributes SAC-D (Satelite de Aplicaciones Cientificas) Service Platform and Ground Station.
Attitude & Orbit Control: Three axis stabilized, nadir pointing; maneuvering thrusters.
Observatory Dimensions (launch config): 2,7m (diameter) and 4,5 m
Communications: S Band Up and Downlink, X Band Data Downlink
Operational Life: 3 years (Aquarius); 5 years (S/P and SAC-D Instruments)
Launch Date: June 10, 2011
Launch Vehicle: Boeing Delta II 7320-10 Launch Vehicle
Launch Site: Vandenberg Air Force Base (VAFB), California, USA
Science Products: 7-day, Monthly and Yearly Global Maps
Data Availability: Through PO.DAAC (NASA / JPL)
