Overview
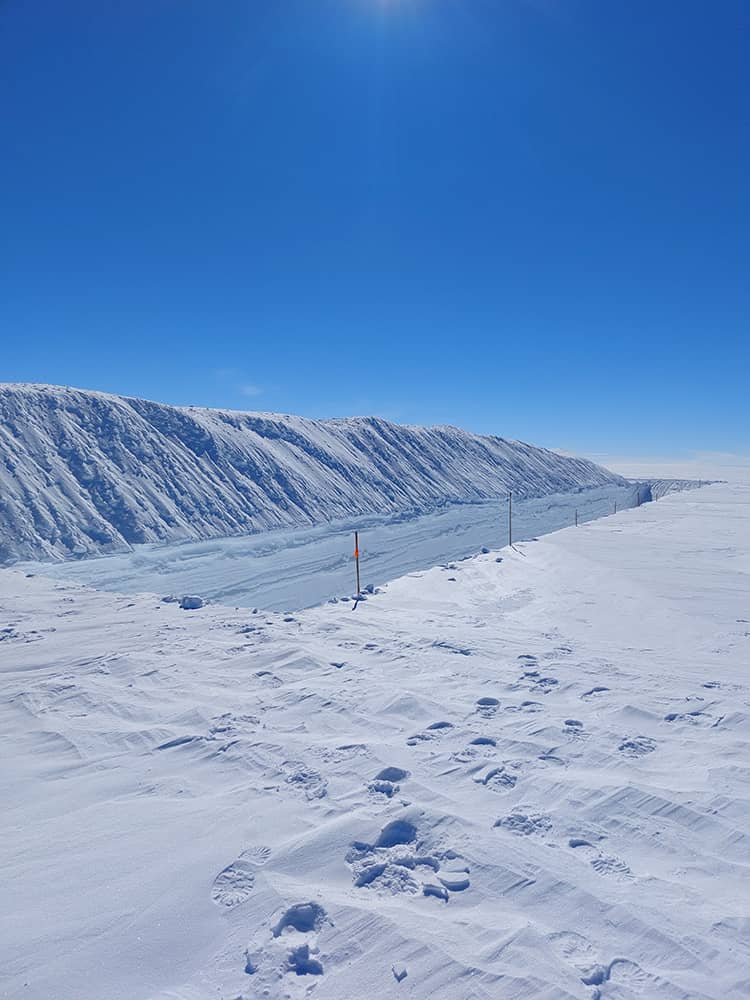

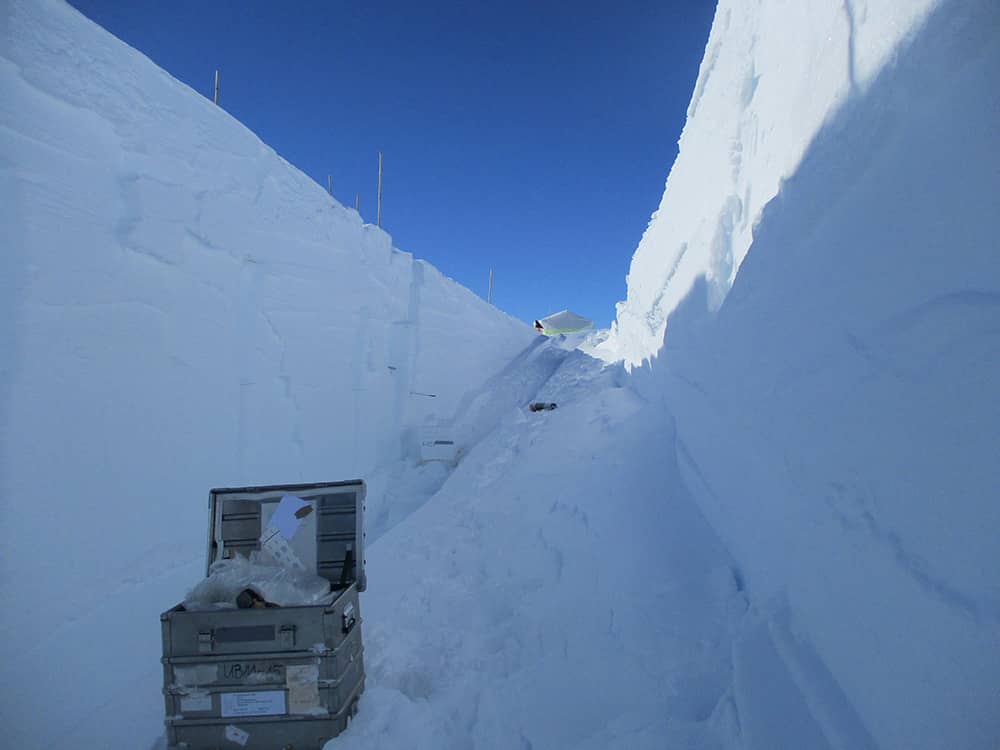
As part of the SNOWISO initiative, our team provides finely resolved, depth- and time-indexed measurements of water isotopologues from short (1-m) snow cores collected at the EastGRIP site on the Greenland Ice Sheet during the summers of 2017–2019. Each profile is accompanied by an applied age–depth model, allowing the isotopic data (δ¹⁸O, δD, and deuterium excess) to be interpreted not only in terms of stratigraphy but also as a seasonal record of snow deposition and modification.
These datasets are particularly valuable for investigating how post-depositional processes—such as sublimation, ventilation, and isotopic diffusion—shape the isotopic composition of snow, thereby influencing the signals preserved in firn and ice cores. In addition, the high-resolution sampling provides a framework for studying snowpack layering, accumulation patterns, and isotopic variability on spatial and temporal scales that are often inaccessible to traditional core analyses. By linking near-surface measurements to broader climatic interpretation, the SNOWISO data support improved understanding of both modern atmospheric processes and the paleoclimate information archived in the Greenland Ice Sheet. All data are openly available for further research, model validation, and interdisciplinary analysis.
Team

Partners
The Geophysical Institute, University of Bergen, Earth and Space Research
Project website
Citations and access

Data may be accessed through Pangaea:
https://doi.pangaea.de/10.1594/PANGAEA.958540
Please use the following citation for the MBCL dataset:
Town, Michael S; Steen-Larsen, Hans Christian; Wahl, Sonja; Faber, Anne-Katrine (2023): Water isotopologues of near-surface polar snow from short (1-m) snow cores, extracted from the EastGRIP site on Greenland Ice Sheet during summers 2017-2019 with age-depth model [dataset publication series]. PANGAEA, https://doi.org/10.1594/PANGAEA.958540
Related publication:
Town, M. S., Steen-Larsen, H. C., Wahl, S., Faber, A.-K., Behrens, M., Jones, T. R., and Sveinbjornsdottir, A.: Post-depositional modification on seasonal-to-interannual timescales alters the deuterium-excess signals in summer snow layers in Greenland, The Cryosphere, 18, 3653–3683, https://doi.org/10.5194/tc-18-3653-2024, 2024.
Funding
This research received the majority of funding from the European Research Council (ERC) under the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation program: Starting Grant – SNOWISO (grant agreement 759526). The simulations and some manuscript writing were funded by Collaborative Research: NSFGEO-NERC: Integrated Characterization of Energy, Clouds, Atmospheric state, and Precipitation at Summit: Measurements along Lagrangian Transects (grant no. 2137083).